 2025.08.28
2025.08.28
 Industry News
Industry News
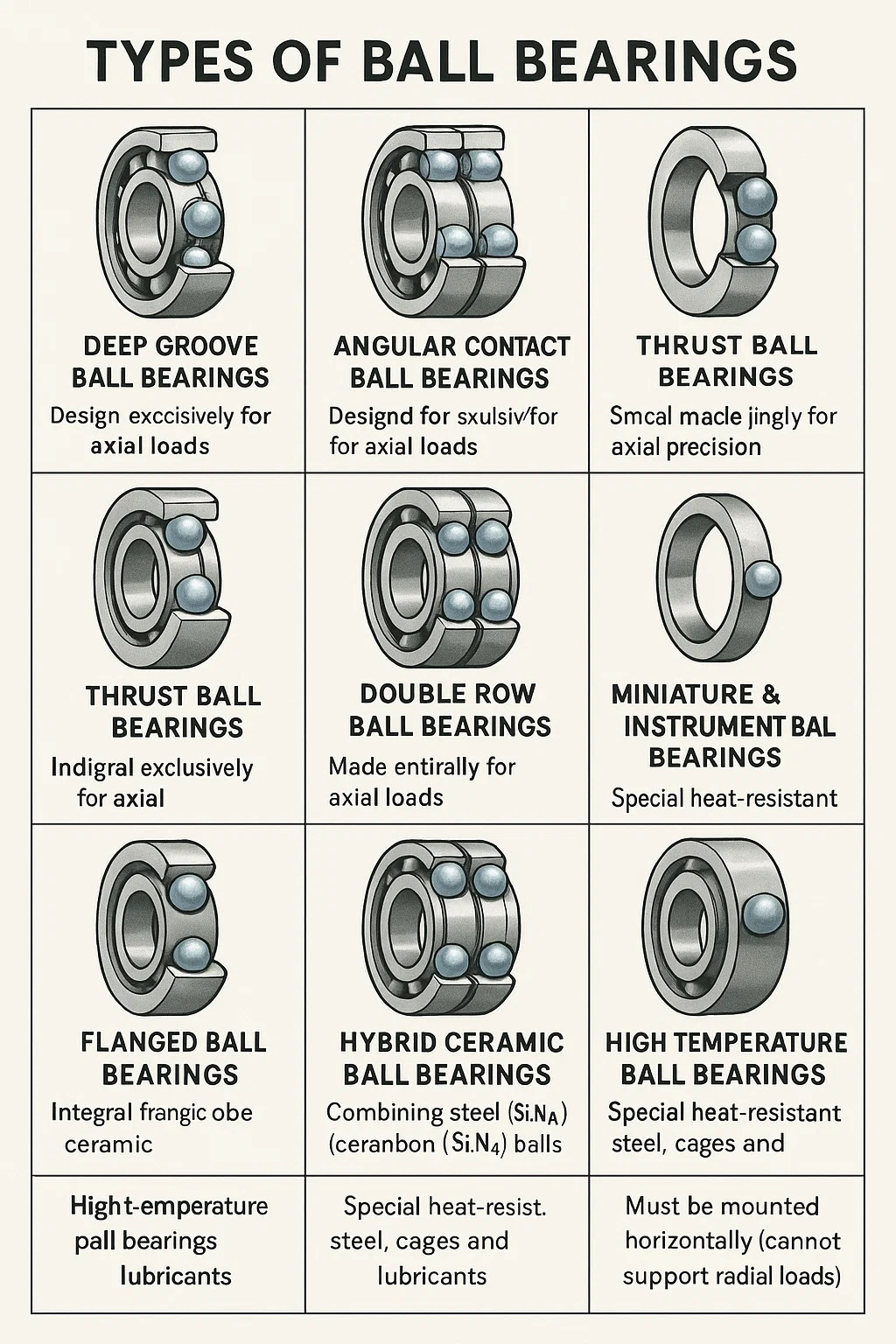
Types of Ball Bearings
1. Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Design: Simple, versatile, with deep raceways in inner/outer rings.
Load Capacity: Handles radial + moderate axial loads (both directions).
Common Uses: Electric motors, appliances, automotive components.
Key Feature: Most widely used; cost-effective for general purposes.
2. Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Design: Asymmetric raceways; designed for combined loads (radial + axial).
Load Capacity: High unidirectional axial load capacity (depends on contact angle).
Common Uses: Machine tool spindles, pumps, gearboxes.
Key Feature: Often used in pairs (back-to-back or face-to-face) to handle thrust in both directions.
3. Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Design: Outer ring has a spherical raceway, allowing misalignment compensation.
Load Capacity: Primarily radial; limited axial load capacity.
Common Uses: Applications with shaft deflection (e.g., long shafts, conveyor systems).
Key Feature: Tolerates misalignment (up to 3°), reducing stress.
4. Thrust Ball Bearings
Design: Designed exclusively for axial loads (no radial load capacity).
Types:
Single-direction: Handles thrust in one direction.
Double-direction: Manages thrust in both directions.
Common Uses: Automotive steering systems, crane hooks, vertical shafts.
Key Feature: Must be mounted horizontally (cannot support radial loads).
5. Double Row Ball Bearings
Design: Two rows of balls for higher radial load capacity than single-row bearings.
Load Capacity: Handles heavy radial loads but limited axial capacity.
Common Uses: Industrial gearboxes, heavy machinery.
Key Feature: More rigid than single-row bearings but less tolerant of misalignment.
6. Miniature & Instrument Ball Bearings
Design: Extremely small (1mm+ bore), high precision.
Load Capacity: Light loads only (radial + minimal axial).
Common Uses: Medical devices, robotics, small motors, drones.
Key Feature: Optimized for high-speed, low-noise applications.
7. Flanged Ball Bearings
Design: Features an integral flange for easy mounting/alignment.
Load Capacity: Similar to deep groove bearings.
Common Uses: Linear motion guides, conveyor rollers.
Key Feature: Simplifies installation by eliminating the need for separate housings.
8. Hybrid Ceramic Ball Bearings
Design: Combines steel rings + ceramic (Si3N4) balls.
Load Capacity: Similar to steel bearings but with higher speed capability.
Common Uses: High-speed spindles, aerospace, racing applications.
Key Feature: Reduced friction, heat resistance, electrical insulation.
9. Stainless Steel Ball Bearings
Design: Made entirely from corrosion-resistant stainless steel (304/316/440C).
Load Capacity: Lower than chrome steel bearings but resists rust/chemicals.
Common Uses: Food processing, marine, medical, and chemical industries.
Key Feature: No coating flaking (hygienic for sensitive environments).
10. High-Temperature Ball Bearings
Design: Uses special heat-resistant steel, cages, and lubricants.
Load Capacity: Standard radial/axial, but operates at 200°C+.
Common Uses: Furnaces, industrial ovens, turbochargers.
Key Feature: Prevents lubricant breakdown & material warping under heat.