 2025.08.18
2025.08.18
 Industry News
Industry News
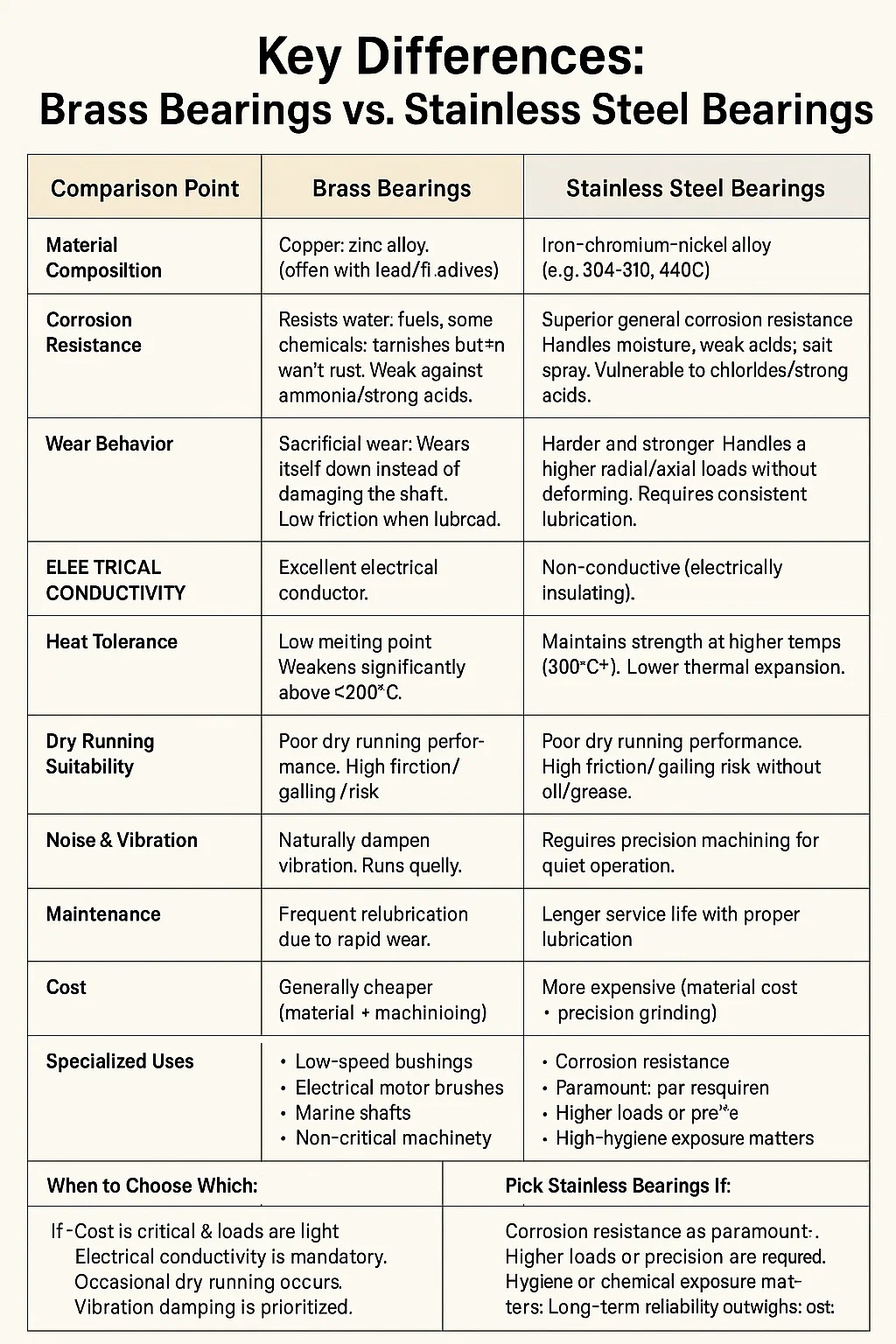
Here's a detailed comparison between brass bearings and stainless steel bearings:
| Comparison Point | Brass Bearings | Stainless Steel Bearings |
| Material Composition | Copper-zinc alloy (often with lead/tin additives) | Iron-chromium-nickel alloy (e.g., 304, 316, 440C) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Resists water, fuels, some chemicals; tarnishes but won’t rust. Weak against ammonia/strong acids. | Superior general corrosion resistance. Handles moisture, weak acids, salt spray. Vulnerable to chlorides/strong acids. |
| Strength & Hardness | Soft material, low load capacity. Prone to deformation under heavy loads. | Harder and stronger. Handles higher radial/axial loads without deforming. |
| Wear Behavior | Sacrificial wear: Wears itself down instead of damaging the shaft. Low friction when lubricated. | Wear-resistant but may gall (adhere to shaft) if under-lubricated. Requires consistent lubrication. |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent electrical conductor. | Non-conductive (electrically insulating). |
| Heat Tolerance | Low melting point. Weakens significantly above ≈200°C. Thermal expansion high. | Maintains strength at higher temps (300°C+). Lower thermal expansion. |
| Dry Running Suitability | Can run temporarily without lubricant (quiet but wears rapidly). | Poor dry running performance. High friction/galling risk without oil/grease. |
| Noise & Vibration | Naturally dampens vibration. Runs quietly. | Requires precision machining for quiet operation. More prone to ringing noise. |
| Maintenance | Frequent relubrication needed due to rapid wear. | Longer service life with proper lubrication. |
| Cost | Generally cheaper (material + machining). | More expensive (material cost + precision grinding). |
| Specialized Uses | • Low-speed bushings• Electrical motor brushes• Marine shafts• Non-critical machinery | • Food/medical equipment• Chemical pumps• Marine hardware• High-hygiene applications |