

Information to be updated




When selecting stainless steel ball bearings, careful consideration must be given to their accuracy. Accuracy directly affects the performance and applicable scenarios of bearings. The following are k...
View MoreWhen choosing stainless steel ball bearings, ensuring size matching is absolutely crucial. Here are several core reasons: Installation feasibility:The bearing must be able to be smoothly installed int...
View MoreDifferent usage environments indeed require the selection of different types of stainless steel ball bearings to ensure optimal performance, lifespan, and safety. The following is a point by point int...
View MoreSingle-row deep groove ball bearing: In-depth analysis of technology and application
——Focus on the innovation and service of Ningbo NBVO Seiko Bearing Co., Ltd
1. What is a single-row deep groove ball bearing? Why has it become a "universal part" in the industrial field?
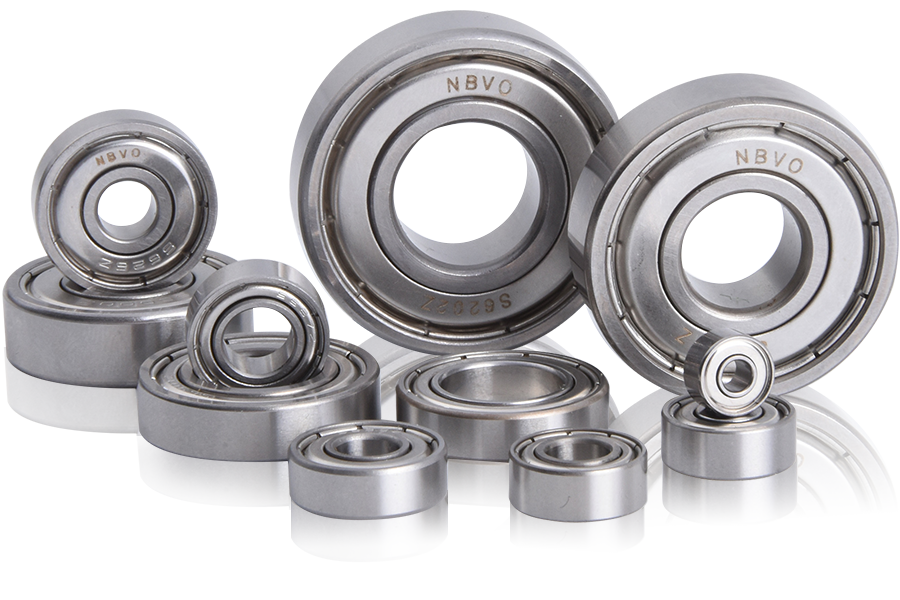
Single-row deep groove ball bearings are one of the most representative structures in rolling bearings. With their deep groove raceway design, they can simultaneously withstand radial and bidirectional axial loads. Its low friction resistance, high speed and low noise make it a core component in the fields of motors, automobile gearboxes, and home appliances. Ningbo NBVO Seiko Bearing Co., Ltd focuses on the research and development and production of such bearings. Its products are known for their high precision, low noise and long life. It is particularly good at manufacturing micro-sized bearings, filling the market gap in the field of high precision.
2. How do single-row deep groove ball bearings cope with harsh working conditions? Where is NBVO Seiko's technological innovation reflected?
In high temperature, high humidity or highly corrosive environments, the wear resistance and fatigue resistance of bearings are crucial. NBVO Seiko has realized the automatic positioning of ball assembly through its independently developed patented "bearing production positioning mechanism" technology (CN222377041U), greatly improving production efficiency and product consistency. In addition, its "bearing grinding device" patent (CN222493400U) optimizes the surface treatment process to ensure the stability of bearings under high-speed operation. These innovations enable NBVO's products to adapt to scenarios with extremely high reliability requirements such as automobiles and medical equipment.
3. Why choose Ningbo NBVO Seiko's products? What is its core competitiveness?
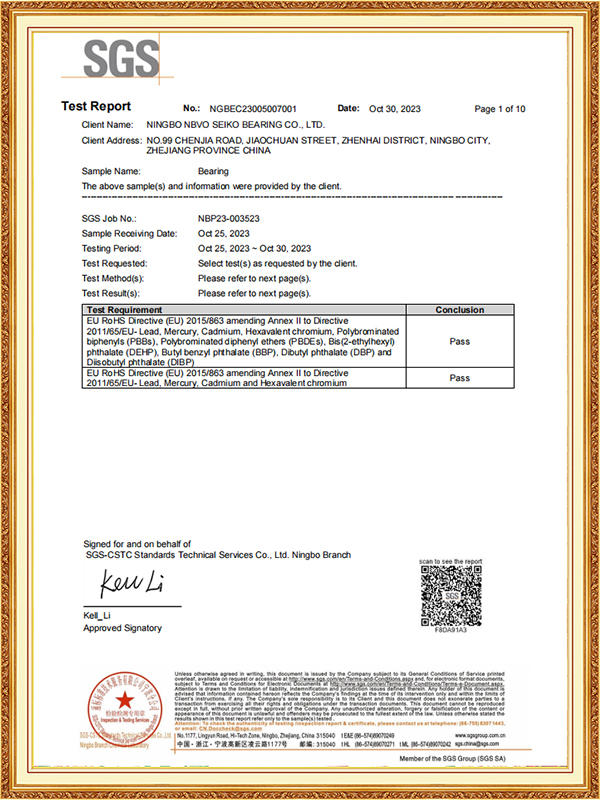
Ningbo NBVO Seiko is not only a national high-tech enterprise, but also has passed ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 quality management system certification, and strictly controls the entire process from raw materials to finished products. Its products use EU RoHS standard materials, and some models can even be customized with stainless steel materials to meet the corrosion resistance requirements of special industries such as food machinery and chemical equipment.
4. From production to delivery, how does Ningbo NBVO Seiko ensure customer needs?
In response to the demand for fast delivery, Ningbo NBVO Seiko provides a "7-day standard product delivery" service, and non-standard products can also be customized within 15-30 days. The company also supports free sample delivery and professional analysis services to help customers accurately match application scenarios. This "customer-centric" concept makes it stand out in the fiercely competitive bearing market.
5. How will single-row deep groove ball bearings develop in the future? What is Ningbo NBVO Seiko's layout?
As industrial equipment develops towards lightweight and intelligent, the accuracy and life requirements of bearings continue to upgrade. Ningbo NBVO Seiko has deployed high-growth fields such as new energy vehicles and robots, and through continuous investment in research and development, it promotes the integrated innovation of bearings and smart sensors. Its goal is not only to become a leading domestic supplier of precision bearings, but also to participate in international high-end market competition and break import dependence.
What is the value of cooperating with Ningbo NBVO Seiko?
Free sample support: Spot samples can be sent quickly to help you verify performance with zero risk.
Flexible production system: From micro to standard bearings, flexible response to diverse needs.
Full-cycle service: From selection recommendations to after-sales maintenance, we provide a one-stop solution.
If you need to learn more about the products and technical details of Ningbo NBVO Seiko Bearing Co., Ltd, please feel free to contact us. We will use our professionalism and innovation to give your equipment a more reliable "power heart". Website