 2025.10.09
2025.10.09
 Industry News
Industry News
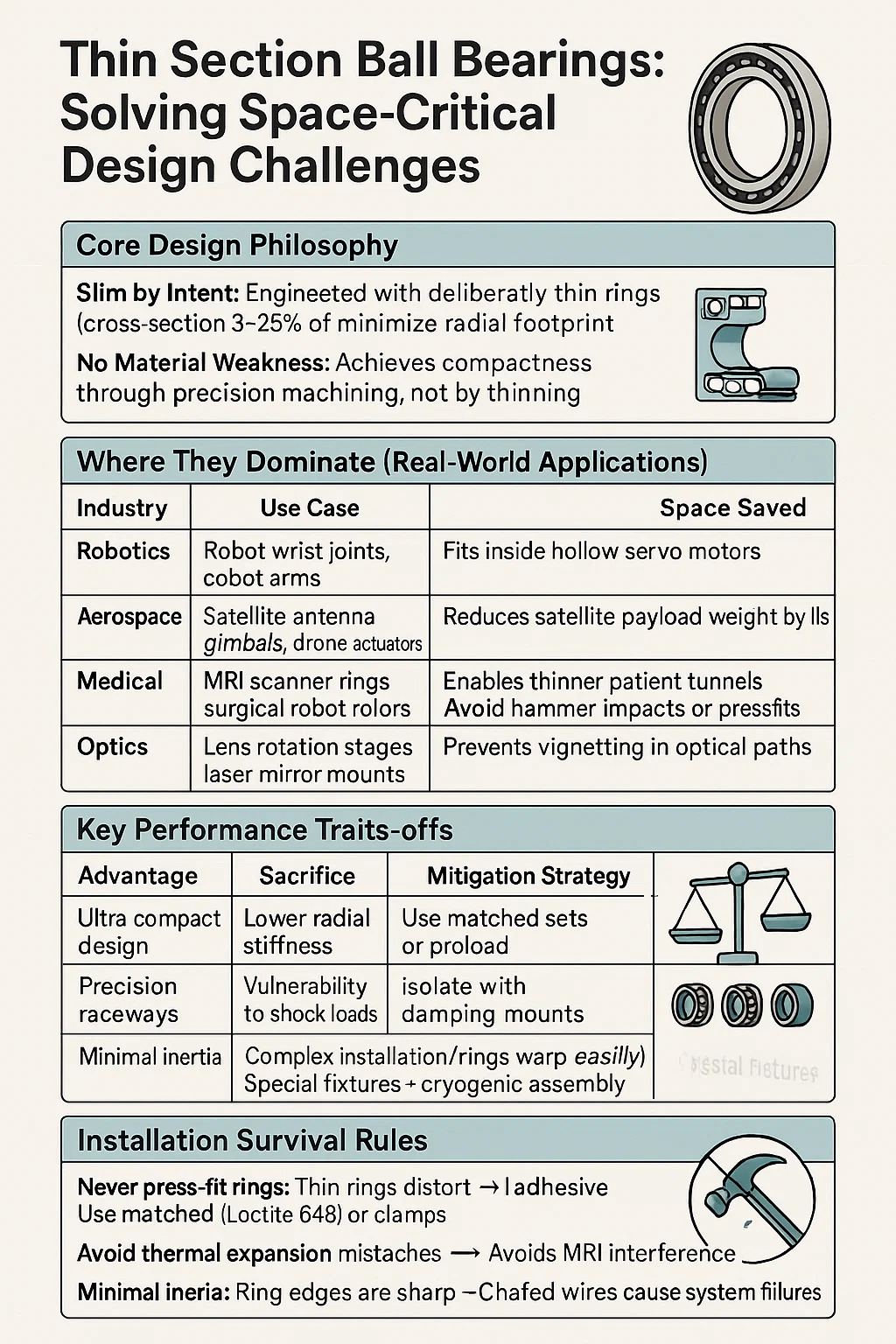
Thin Section Ball Bearings: Solving Space-Critical Design Challenges
1. Core Design Philosophy
"Slim by Intent": Engineered with deliberately thin rings (cross-section 3–25% of bore size) to minimize radial footprint.
No Material Weakness: Achieves compactness through precision machining, not by thinning existing bearings.
2. Where They Dominate (Real-World Applications)
| Industry | Use Case | Space Saved |
|---|---|---|
| Robotics | Robot wrist joints, cobot arms | Fits inside hollow servo motors |
| Aerospace | Satellite antenna gimbals, drone actuators | Reduces satellite payload weight by lbs |
| Medical | MRI scanner rings, surgical robot rotors | Enables thinner patient tunnels |
| Optics | Lens rotation stages, laser mirror mounts | Prevents vignetting in optical paths |
3. Key Performance Traits
Space Efficiency: For a 100mm bore, standard bearing ≈ 140mm OD; thin section ≈ 110mm OD.
Weight Reduction: 50–70% lighter than equivalent standard bearings.
Precision Focus: Typically ABEC 5+ tolerance – mandatory for misalignment-sensitive apps.
Load Limitation: Handles moderate radial loads only – avoid hammer impacts or press fits.
4. Critical Engineering Trade-offs
| Advantage | Sacrifice | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-compact design | Lower radial stiffness | Use matched sets or preload |
| Precision raceways | Vulnerability to shock loads | Isolate bearings with damping mounts |
| Minimal inertia | Complex installation (rings warp easily) | Special fixtures + cryogenic assembly |
5. Material Options Dictate Use
Chrome Steel (GCR15): Default for dry/clean environments (e.g., lab equipment).
Stainless Steel (440C): Medical/outdoor use – avoids MRI interference & corrosion.
Hybrid Ceramic: High-speed CT scanners – non-magnetic + electrical insulation.
6. Installation Survival Rules
Never press-fit rings: Thin rings distort → Use adhesive (Loctite 648) or clamps.
Avoid thermal expansion mismatches: Aluminum housings + steel bearings = binding.
Shield cables/wires: Ring edges are sharp – chafed wires cause system failures.